Structure
To topThis assumes you have created and filled out a taxonomy.
Your Taxonomy API, as well as your Entity API and Data Cleaning API, is automatically created when you initially create a taxonomy.
By default your API is private, not publicly visible to others. It is secured using modern best practices and resides on AWS (Amazon Web Services), supporting high up time and reliability.
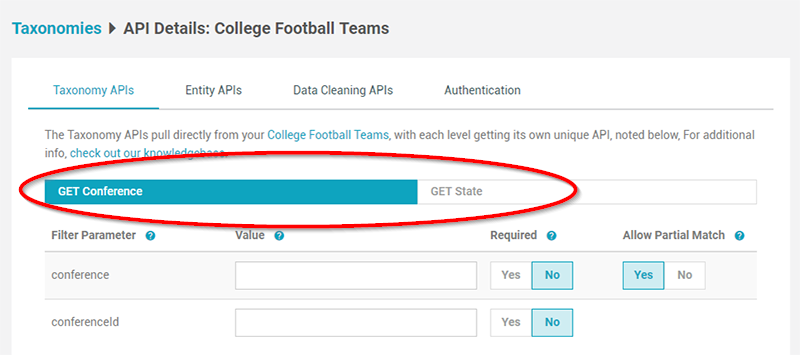
First, you will notice that there is a unique group of endpoints, GET calls, created for each taxonomy level See an example below, of a College Football Team API that has two taxonomy levels: “Conference” and “State”.
Filter Parameters
To topWithin each GET call, you’ll notice a table containing filter parameters. A filter parameter is used for filtering the content of the respective taxonomy level.
Also notice that for each taxonomy level and entity, you’ll see two filter parameters: one for filtering by normal text/string content, as well as an “ID” filter, which allows you to filter by the numeric ID of a taxonomy level or entity.
Filter Options
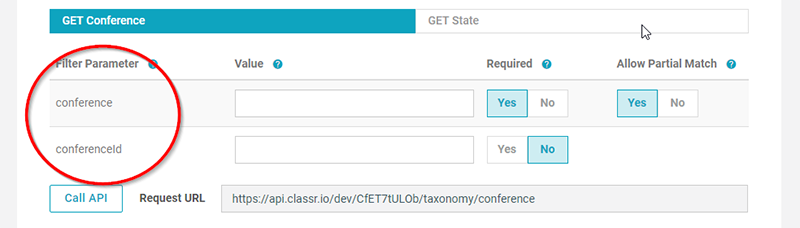
To topNext to each filter parameter you’ll see up to three options:
- Value
- Required
- Allow Partial Match
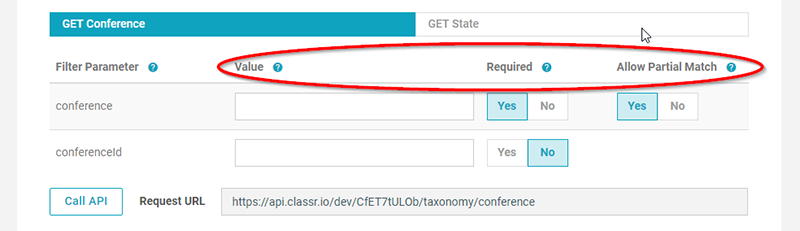
Value: this is where you put in the content of your filter, for testing purposes in the API interface online only. Value for an ID filter will be a number (call the API to see). The Value for a non-ID parameter, e.g. “Conference” above, will be a string, allowing you to filter by the actual name of each taxonomy level.
Required: this is “No” by default. When flipped to “Yes”, it requires something to be entered into the “value” for that respective filter parameter. Note, by default, filter parameters only show his on exact match.
Allow Partial Match: this is “No” by default. When flipped to “Yes”, it allows filtering to happen on a partial match. You will only see Partial Match on non-ID filter parameters (ID-based filter parameters need a number and use exact match, only).
API URL Structure
To topThe Taxonomy API is structured just like the Entity API. Here’s an example of a sample API call:
https://api.classr.io/CfKR7tULOb/taxonomy/taxonomylevelname
CfKR7tULOb: this is the automatically generated hashcode, unique to your account
“taxonomylevelname”: this is representative of the taxonomy level’s name. It is a transformation of your taxonomy level’s name: lowercase and with spaces removed.
Response Body Format
To topThe format represents the following below.
[
{
“conference”: “ACC”,
“conferenceId”: 2
},
{
“conference”: “SEC”,
“conferenceId”: 6
},
{
Note the format of the response body:
- Note, the response body displays the content of the taxonomy level being called. Additionally, the lower you go down the taxonomy levels, you will see the level called as well as all upper levels of the taxonomy.
- Each attribute in the response body shows both the name as well as the autogenerated ID for that ID.
FAQ
To topWhen is my Taxonomy API created?
The moment you finish your taxonomy process, the API is automatically created.
How long will it take for API calls to show up in my usage count (on your home dashboard)?
Around a minute.